最近有用到水下气泡上升效果,因此在网上查了一下资料,结果还真找到了,就是这篇文章 [Android实例] 水下气泡上升界面效果, 不过这篇文章所附带的示例代码是有些问题的,例如View移除后,线程没有正确关闭,锁屏后再打开屏幕,气泡会挤成一团等问题,因此我在它的原理基础上稍为进行了一些调整和修改,解决了这些问题,它可以实现下面这样的效果:
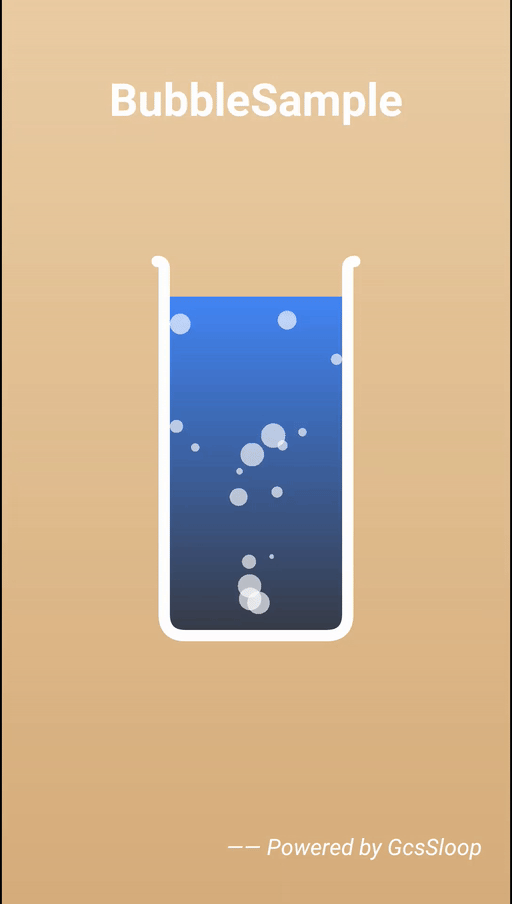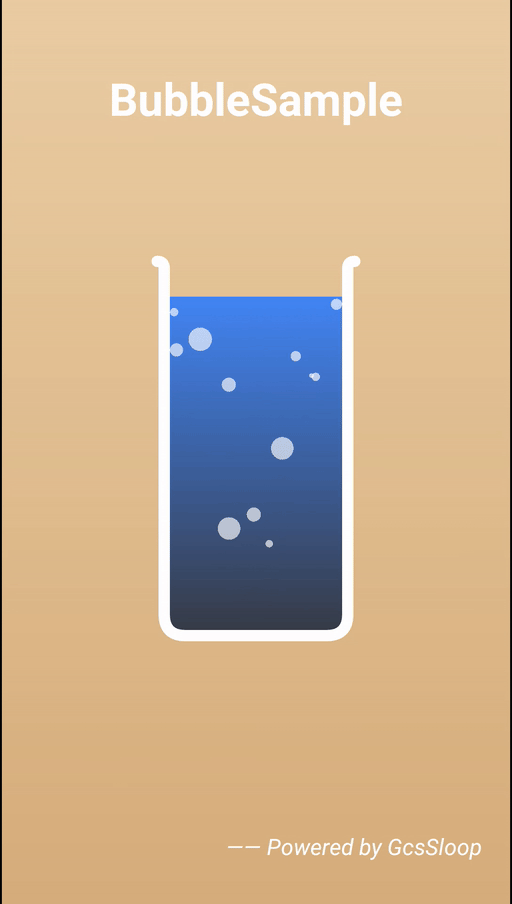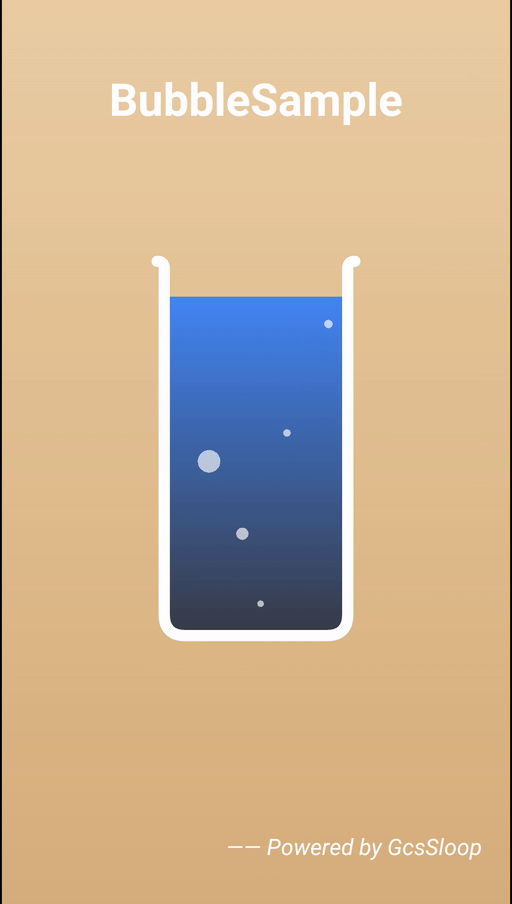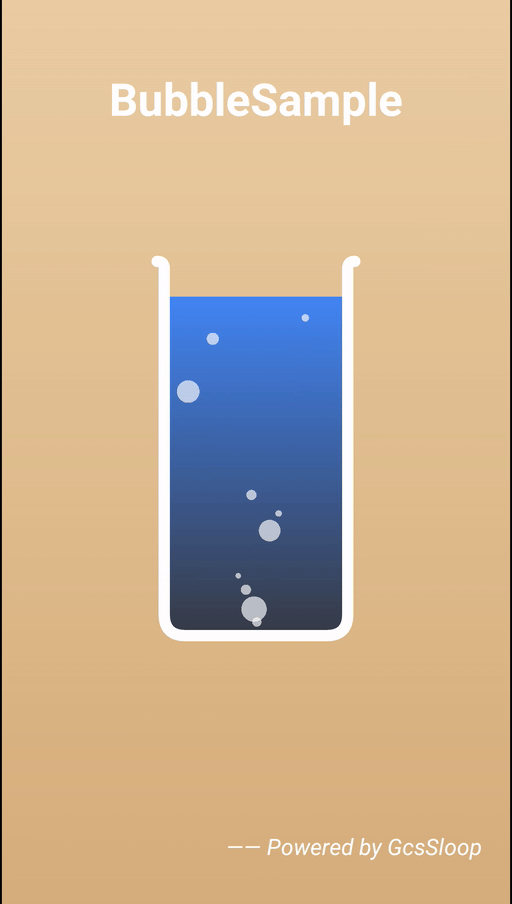
0. 基本原理
气泡效果的基本原理非常简单,其实所谓的气泡就是一个个的半透明圆而已,它的基本逻辑如下:
- 如果当前圆的数量没有超过数量上限,则随机生成半径不同的圆。
- 设定这些圆的初始位置。
- 随机设定垂直向上平移速度。
- 随机设定水平平移速度。
- 不断的刷新圆的位置然后绘制。
- 将超出显示区域的圆进行移除。
- 不断重复。
原理可以说非常简单,但是也有一些需要注意的地方,尤其是线程,最容易出问题。
在原始的 demo 中,直接把线程创建和计算逻辑直接放到了 onDraw 里面,而且没有关闭线程,这自然会导致很多问题的发生。没有关闭线程会造成View的内存泄露,而把计算逻辑放在 onDraw 里面则会加大绘制的负担,拖慢刷新速度,在机能较弱的情况下会导致明显卡顿的发生。而解决这些问题的最好办法则是专事专办,将合适的内容放在合适的位置,下面来看一下具体的代码实现。
1. 代码实现
1.1 定义气泡
气泡效果我们关心的属性并不多,主要有这几种:半径、坐标、上升速度、水平平移速度。由于我们只在 View 内部使用,因此直接创建一个内部类,然后在内部类中定义这些属性。
private class Bubble {
int radius; // 气泡半径
float speedY; // 上升速度
float speedX; // 平移速度
float x; // 气泡x坐标
float y; // 气泡y坐标
}
1.2 生命周期处理
由于需要用线程来进行计算和控制刷新,就少不了开启和关闭线程,这个自然要符合 View 的生命周期,因此我在 View 被添加到界面上时开启了一个线程用于生成气泡和刷新气泡位置,然后在 View 从界面上移除的时候关闭了这个线程。
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
startBubbleSync();
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
stopBubbleSync();
}
1.3 开启线程
开启线程非常简单,就是简单的创建了一个线程,然后在里面添加了一个 while 死循环,然后不停的执行 休眠、创建气泡、刷新气泡位置、申请更新UI 等操作。
这里没有用变量来控制循环,而是监听了中断事件,在当拦截到 InterruptedException 的时候,使用 break 跳出了死循环,因此线程也就结束了,方法简单粗暴。
// 开始气泡线程
private void startBubbleSync() {
stopBubbleSync();
mBubbleThread = new Thread() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(mBubbleRefreshTime);
tryCreateBubble();
refreshBubbles();
postInvalidate();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Bubble线程结束");
break;
}
}
}
};
mBubbleThread.start();
}
1.4 关闭线程
由于线程运行时监听了 interrupt 中断,这里直接使用 interrupt 通知线程中断就可以了。
// 停止气泡线程
private void stopBubbleSync() {
if (null == mBubbleThread) return;
mBubbleThread.interrupt();
mBubbleThread = null;
}
1.5 创建气泡
为了防止气泡数量过多而占用太多的性能,因此在创建气泡之前需要先判断当前已经有多少个气泡,如果已经有足够多的气泡了,则不再创建新的气泡。
同时,为了让气泡产生过程看起来更合理,在气泡数量没有达到上限之前,会随机的创建气泡,以防止气泡扎堆出现,因此设立了一个随机项,生成的随机数大于 0.95 的时候才生成气泡,让气泡生成过程慢一些。
创建气泡的过程也很简单,就是随机的在设定范围内生成一些属性,然后放到 List 中而已。
PS:这里使用了一些硬编码和魔数,属于不太好的习惯。不过由于应用场景固定,这些参数需要调整的概率比较小,影响也不大。
// 尝试创建气泡
private void tryCreateBubble() {
if (null == mContentRectF) return;
if (mBubbles.size() >= mBubbleMaxSize) {
return;
}
if (random.nextFloat() < 0.95) {
return;
}
Bubble bubble = new Bubble();
int radius = random.nextInt(mBubbleMaxRadius - mBubbleMinRadius);
radius += mBubbleMinRadius;
float speedY = random.nextFloat() * mBubbleMaxSpeedY;
while (speedY < 1) {
speedY = random.nextFloat() * mBubbleMaxSpeedY;
}
bubble.radius = radius;
bubble.speedY = speedY;
bubble.x = mWaterRectF.centerX();
bubble.y = mWaterRectF.bottom - radius - mBottleBorder / 2;
float speedX = random.nextFloat() - 0.5f;
while (speedX == 0) {
speedX = random.nextFloat() - 0.5f;
}
bubble.speedX = speedX * 2;
mBubbles.add(bubble);
}
1.6 刷新气泡位置
这里主要做了两项工作:
- 将超出显示区域的气泡进行移除。
- 计算新的气泡显示位置。
可以看到这里没有直接使用原始的List,而是复制了一个 List 进行遍历,这样做主要是为了规避 ConcurrentModificationException 异常,(对Vector、ArrayList在迭代的时候如果同时对其进行修改就会抛出 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常)。
对复制的 List 进行遍历,然后对超出显示区域的 Bubble 进行移除,对没有超出显示区域的 Bubble 位置进行了刷新。可以看到,这里逻辑比较复杂,有各种加减计算,是为了解决气泡飘到边缘的问题,防止气泡飘出水所在的范围。
// 刷新气泡位置,对于超出区域的气泡进行移除
private void refreshBubbles() {
List<Bubble> list = new ArrayList<>(mBubbles);
for (Bubble bubble : list) {
if (bubble.y - bubble.speedY <= mWaterRectF.top + bubble.radius) {
mBubbles.remove(bubble);
} else {
int i = mBubbles.indexOf(bubble);
if (bubble.x + bubble.speedX <= mWaterRectF.left + bubble.radius + mBottleBorder / 2) {
bubble.x = mWaterRectF.left + bubble.radius + mBottleBorder / 2;
} else if (bubble.x + bubble.speedX >= mWaterRectF.right - bubble.radius - mBottleBorder / 2) {
bubble.x = mWaterRectF.right - bubble.radius - mBottleBorder / 2;
} else {
bubble.x = bubble.x + bubble.speedX;
}
bubble.y = bubble.y - bubble.speedY;
mBubbles.set(i, bubble);
}
}
}
1.7 绘制气泡
绘制气泡同样简单,就是遍历 List,然后画圆就行了。
这里同样复制了一个新的 List 进行操作,不过这个与上面的原因不同,是为了防止多线程问题。由于在绘制的过程中,我们的计算线程可能会对原始 List 进行更新,可能导致异常的发生。为了避免这样的问题,就复制了一个 List 出来用于遍历绘制。
// 绘制气泡
private void drawBubble(Canvas canvas) {
List<Bubble> list = new ArrayList<>(mBubbles);
for (Bubble bubble : list) {
if (null == bubble) continue;
canvas.drawCircle(bubble.x, bubble.y,
bubble.radius, mBubblePaint);
}
}
2. 完整代码
完整的示例代码非常简单,所以直接贴在了正文中,同时,你也可以从文末下载完整的项目代码。
public class BubbleView extends View {
private int mBubbleMaxRadius = 30; // 气泡最大半径 px
private int mBubbleMinRadius = 5; // 气泡最小半径 px
private int mBubbleMaxSize = 30; // 气泡数量
private int mBubbleRefreshTime = 20; // 刷新间隔
private int mBubbleMaxSpeedY = 5; // 气泡速度
private int mBubbleAlpha = 128; // 气泡画笔
private float mBottleWidth; // 瓶子宽度
private float mBottleHeight; // 瓶子高度
private float mBottleRadius; // 瓶子底部转角半径
private float mBottleBorder; // 瓶子边缘宽度
private float mBottleCapRadius; // 瓶子顶部转角半径
private float mWaterHeight; // 水的高度
private RectF mContentRectF; // 实际可用内容区域
private RectF mWaterRectF; // 水占用的区域
private Path mBottlePath; // 外部瓶子
private Path mWaterPath; // 水
private Paint mBottlePaint; // 瓶子画笔
private Paint mWaterPaint; // 水画笔
private Paint mBubblePaint; // 气泡画笔
public BubbleView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public BubbleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public BubbleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mWaterRectF = new RectF();
mBottleWidth = dp2px(130);
mBottleHeight = dp2px(260);
mBottleBorder = dp2px(8);
mBottleRadius = dp2px(15);
mBottleCapRadius = dp2px(5);
mWaterHeight = dp2px(240);
mBottlePath = new Path();
mWaterPath = new Path();
mBottlePaint = new Paint();
mBottlePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mBottlePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mBottlePaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mBottlePaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
mBottlePaint.setStrokeWidth(mBottleBorder);
mWaterPaint = new Paint();
mWaterPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
initBubble();
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mContentRectF = new RectF(getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop(), w - getPaddingRight(), h - getPaddingBottom());
float bl = mContentRectF.centerX() - mBottleWidth / 2;
float bt = mContentRectF.centerY() - mBottleHeight / 2;
float br = mContentRectF.centerX() + mBottleWidth / 2;
float bb = mContentRectF.centerY() + mBottleHeight / 2;
mBottlePath.reset();
mBottlePath.moveTo(bl - mBottleCapRadius, bt - mBottleCapRadius);
mBottlePath.quadTo(bl, bt - mBottleCapRadius, bl, bt);
mBottlePath.lineTo(bl, bb - mBottleRadius);
mBottlePath.quadTo(bl, bb, bl + mBottleRadius, bb);
mBottlePath.lineTo(br - mBottleRadius, bb);
mBottlePath.quadTo(br, bb, br, bb - mBottleRadius);
mBottlePath.lineTo(br, bt);
mBottlePath.quadTo(br, bt - mBottleCapRadius, br + mBottleCapRadius, bt - mBottleCapRadius);
mWaterPath.reset();
mWaterPath.moveTo(bl, bb - mWaterHeight);
mWaterPath.lineTo(bl, bb - mBottleRadius);
mWaterPath.quadTo(bl, bb, bl + mBottleRadius, bb);
mWaterPath.lineTo(br - mBottleRadius, bb);
mWaterPath.quadTo(br, bb, br, bb - mBottleRadius);
mWaterPath.lineTo(br, bb - mWaterHeight);
mWaterPath.close();
mWaterRectF.set(bl, bb - mWaterHeight, br, bb);
LinearGradient gradient = new LinearGradient(mWaterRectF.centerX(), mWaterRectF.top,
mWaterRectF.centerX(), mWaterRectF.bottom, 0xFF4286f4, 0xFF373B44, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mWaterPaint.setShader(gradient);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawPath(mWaterPath, mWaterPaint);
canvas.drawPath(mBottlePath, mBottlePaint);
drawBubble(canvas);
}
//--- 气泡效果 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
startBubbleSync();
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
stopBubbleSync();
}
private class Bubble {
int radius; // 气泡半径
float speedY; // 上升速度
float speedX; // 平移速度
float x; // 气泡x坐标
float y; // 气泡y坐标
}
private ArrayList<Bubble> mBubbles = new ArrayList<>();
private Random random = new Random();
private Thread mBubbleThread;
// 初始化气泡
private void initBubble() {
mBubblePaint = new Paint();
mBubblePaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
mBubblePaint.setAlpha(mBubbleAlpha);
}
// 开始气泡线程
private void startBubbleSync() {
stopBubbleSync();
mBubbleThread = new Thread() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(mBubbleRefreshTime);
tryCreateBubble();
refreshBubbles();
postInvalidate();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Bubble线程结束");
break;
}
}
}
};
mBubbleThread.start();
}
// 停止气泡线程
private void stopBubbleSync() {
if (null == mBubbleThread) return;
mBubbleThread.interrupt();
mBubbleThread = null;
}
// 绘制气泡
private void drawBubble(Canvas canvas) {
List<Bubble> list = new ArrayList<>(mBubbles);
for (Bubble bubble : list) {
if (null == bubble) continue;
canvas.drawCircle(bubble.x, bubble.y,
bubble.radius, mBubblePaint);
}
}
// 尝试创建气泡
private void tryCreateBubble() {
if (null == mContentRectF) return;
if (mBubbles.size() >= mBubbleMaxSize) {
return;
}
if (random.nextFloat() < 0.95) {
return;
}
Bubble bubble = new Bubble();
int radius = random.nextInt(mBubbleMaxRadius - mBubbleMinRadius);
radius += mBubbleMinRadius;
float speedY = random.nextFloat() * mBubbleMaxSpeedY;
while (speedY < 1) {
speedY = random.nextFloat() * mBubbleMaxSpeedY;
}
bubble.radius = radius;
bubble.speedY = speedY;
bubble.x = mWaterRectF.centerX();
bubble.y = mWaterRectF.bottom - radius - mBottleBorder / 2;
float speedX = random.nextFloat() - 0.5f;
while (speedX == 0) {
speedX = random.nextFloat() - 0.5f;
}
bubble.speedX = speedX * 2;
mBubbles.add(bubble);
}
// 刷新气泡位置,对于超出区域的气泡进行移除
private void refreshBubbles() {
List<Bubble> list = new ArrayList<>(mBubbles);
for (Bubble bubble : list) {
if (bubble.y - bubble.speedY <= mWaterRectF.top + bubble.radius) {
mBubbles.remove(bubble);
} else {
int i = mBubbles.indexOf(bubble);
if (bubble.x + bubble.speedX <= mWaterRectF.left + bubble.radius + mBottleBorder / 2) {
bubble.x = mWaterRectF.left + bubble.radius + mBottleBorder / 2;
} else if (bubble.x + bubble.speedX >= mWaterRectF.right - bubble.radius - mBottleBorder / 2) {
bubble.x = mWaterRectF.right - bubble.radius - mBottleBorder / 2;
} else {
bubble.x = bubble.x + bubble.speedX;
}
bubble.y = bubble.y - bubble.speedY;
mBubbles.set(i, bubble);
}
}
}
private float dp2px(float dpValue) {
return TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, dpValue, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
3. 结语
由于本项目是一个示例性质的项目,因此设计的比较简单,结构也是简单粗暴,并没有经过精心的雕琢,存在一些疏漏也说不定,如果大家觉得逻辑上存在问题或者有什么疑惑,欢迎在下面(公众号、小专栏)的评论区留言。
公众号查看到该文章的可以通过点击【阅读原文】下载到所需的示例代码,非公众号阅读的可以从文末或者文初下载到示例项目。


